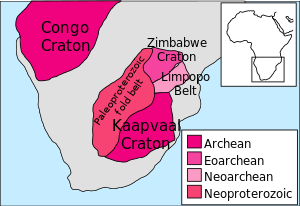
The Zimbabwe Craton is an area in Southern Africa of ancient continental crust, being a part of the ancient continent of Western Gondwana, with rocks dating back to the early Archean Eon, possibly as early as 3.46 billion years ago (Ga.).[1] The craton is named after the country of Zimbabwe where the majority of the craton is. The rocks of the Zimbabwe Craton are separated from the rocks of the Kaapvaal Craton to the southeast by the 250 kilometres (160 mi) wide Limpopo Belt of granulite facies tectonites. The Limpopo belt formed contemporaneously with the Zimbabwe and Kaapvaal cratons, but remained geologically active until much later. It was only in the late Archean, ca. 2.8-2.5 Ga., that the two cratons were stabilized together and that high-grade metamorphism ceased in the Limpopo Belt. North of the Zimbabwe Craton is the Zambezi Belt.[2]
- ^ Wilson, J. F.; Nesbitt, R. W. & Fanning, C. M. (1995). "Zircon geochronology of Archaean felsic sequences in the Zimbabwe Craton: a revision of greenstone stratigraphy and a model for crustal growth". In Coward, M. P. & Ries, A. C. (eds.). Early Precambrian processes. Geological Society Special Publications, issue 95. London: Geological Society of London. pp. 109–126. ISBN 978-1-897799-36-9.
- ^ Jelsma, H. A. and Dirks, P. H. G. M. (2002). "Neoarchean Tectonic Evolution of the Zimbabwe Craton". In Fowler, C. M. R.; Ebinger, C. L.; Hawkesworth, C. J. (eds.). The Early Earth: Physical, Chemical and Biological Development. Geological Society Special Publications, issue 199. London: Geological Society of London. pp. 183–211. ISBN 978-1-86239-109-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)