 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
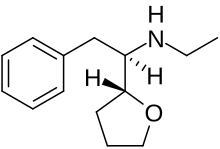
| Formula | C14H21NO |
| Molar mass | 219.328 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Zylofuramine[1] is a stimulant drug. It was developed in 1961,[2][3] and was intended for use as an appetite suppressant and for the treatment of senile dementia in the elderly, but there is little information about it and it does not appear to have ever been marketed.[4]
Its chemical structure has a similarity to other N-ethyl substituted stimulant drugs such as ethylamphetamine and N-ethylhexedrone.
- ^ US patent 3091621, Clarke RL, "Alpha-Aryl or Aralkyl Tetrahydrofurfurylamines", issued 1963-05-28, assigned to Sterling Drugs
- ^ Clarke RL, Harris LS (January 1962). "α-Benzyltetrahydrofurfurylamines -- A New Series of Psychomotor Stimulants. I". Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. 5 (1): 77–95. doi:10.1021/jm01236a010. PMID 14046619.
- ^ Clarke RL, Tullar BF, Harris LS (March 1962). "α-Benzyltetrahydrofurfurylamines -- A New Series of Psychomotor Stimulants. II. Resolution of Isomers". Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. 5 (2): 362–72. doi:10.1021/jm01237a014. PMID 14051912.
- ^ Harris LS, Clarke RL, Dembinski JR (December 1963). "α-Benzyltetrahydrofurfurylamines -- A New Series of Psychomotor Stimulants. III. The Pharmacology of D-Threo α-Benzyl-N-Ethyltetrahydrofurfurylamine (Zylofuramine)". Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie. 146: 392–405. PMID 14099588.